
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
SOLARIS centre
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
Researchers show that an artificial protein structure can be used to precisely arrange gold nanoparticles in three dimensions
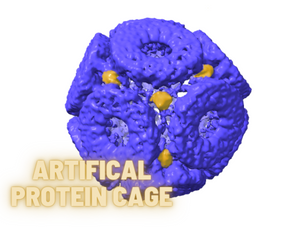
Metal nanoparticles have a wide variety of applications many of which stem from the fact that extremely small particles a few nanometres to 10’s of nanometres in diameter can have very different properties from those of the same material at a larger scale (a nanometre is just a billionth of a metre). Such particles are used as catalysts, coloring agents and can even make antibacterial coatings. Some effects are due to the pattern of the particles and the spacing between them, but these are very difficult to control and particles are typically used in solution where they randomly move around like motes of dust in the air. In the current work, scientists based at the Bionanoscience and Biochemistry Laboratory at the Malopolska Centre of Biotechnology (MCB), Jagiellonian University showed that an artificial protein structure, a hollow sphere called a TRAP-cage, was able to act as a scaffold and provide regular-spaced points of attachment for small gold nanoparticles. “TRAP-cage is itself tiny, but at around 15 nm in diameter is still big enough to attach multiple gold nanoparticles” explained Jonathan Heddle the head of the lab, “The protein cage is made of 12 rings, so overall it looks a little like a 12-sided dice – a dodecahedron.” The researchers showed that there are spaces equivalent to the corners of the dodecahedron that offer just the right environment to snugly fit the gold nanoparticles inside. As a result, instead of randomly floating around, the particles appear to be constrained into a fixed three-dimensional pattern. It is hoped that the ability to arrange metal nanoparticles in this way may be developed further to produce new materials with useful properties.
The MCB team worked together with international collaborators Bernard Piette at The Department of Mathematical Sciences, The University of Durham, UK and the laboratory of Wouter Roos, Zernike Institute for Advanced Materials at The University of Groningen, The Netherlands. They also used the cryo-electron microscope facilities at the Solaris National Radiation Synchrotron Centre, Poland.
Written by: Karolina Majsterkiewicz, Artur Biela, Jonathan Heddle
The paper was published in Nano Letters and can be accessed here:
Heddle Lab homepage: www.heddlelab.org
Heddle Lab Facebook: https://www.facebook.com/heddlelab
Heddle Lab Twitter: @HeddleLab
Image Description: The structure of the protein cage (purple) with three of the embedded gold nanoparticles highlighted (yellow)
Image credit: Jonathan Heddle
