
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
SOLARIS centre
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
Spin-polarization of topological crystalline and trivial insulator films

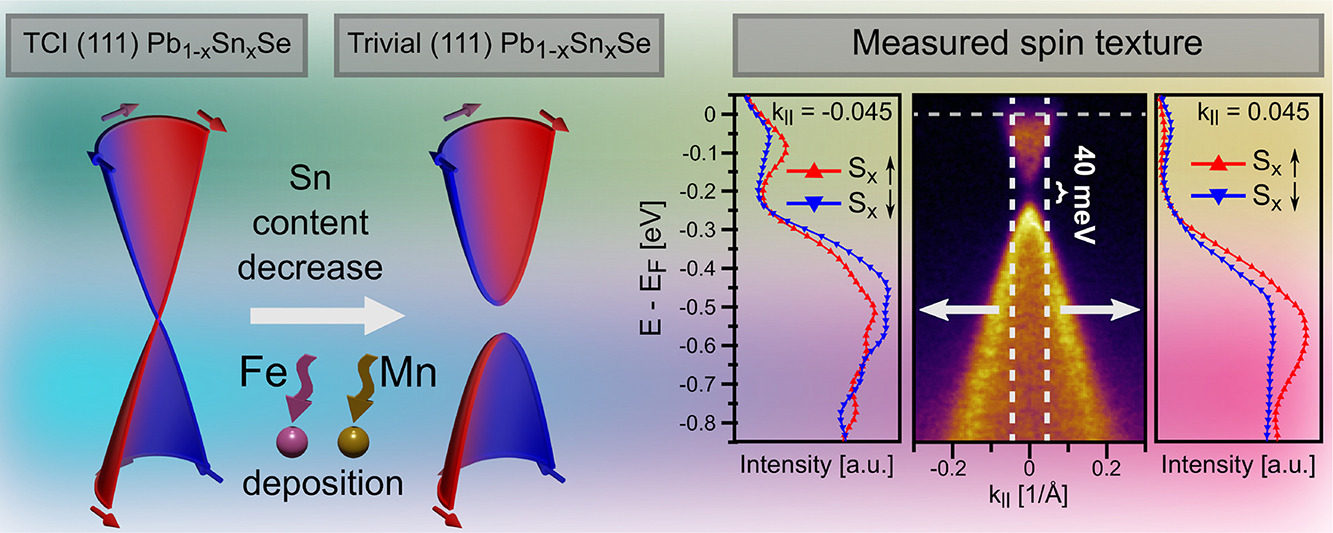
Researchers from MagTop IF PAN in collaboration with scientists from PHELIX beamline at the SOLARIS Centre investigated electronic and spin structure in films of topological crystalline insulator across topological - normal insulator transition manifesting itself as band gap opening in the band structure. Using spin-resolved photoelectron spectroscopy they revealed helical spin-polarization presence not only in the topologically non-trivial phase but also in the trivial insulator state. This potentially expands the range of materials suitable for spintronic applications and provides new knowledge about the spin and electronic structure of topological materials.
Topological crystalline insulators (TCI)s are a class of materials where the helicity of surface states is protected by crystal symmetry. TCIs are highly sensitive to external modifications, thus providing a versatile platform for studying topological transitions. In this work (111)-oriented films of Pb1-xSnxSe were studied. Samples were obtained by Molecular Beam Epitaxy (MBE), advanced synthesis techniques with monolayer thickness control accuracy. MBE is used for the preparation of systems in which materials with different properties are combined owing to epitaxial adjustment to the crystal structure of the substrate. Going through TCI – normal insulator transition in (111)-oriented Pb1-xSnxSe films, we have discovered that the helical spin structure of surface states persists even in a trivial insulator state. Further, we have shown that TCI-normal transition can be induced not only by rising the temperature or reducing Sn content, but also by depositing transition metals on the TCI surface. We also have demonstrated that, in the latter case, the observed gaping of the surface states is caused by a change in surface composition and not by magnetism. This knowledge is important for the fabrication of real hybrid transition metal/TCI spintronic devices.
Link to the publication below:
Turowski B, Kazakov A, Rudniewski R, et al.
Appl Surf Sci. 2023;610:155434. doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2022.155434
Written by: Valentine Volobuev, Magdalena Szczepanik, Tomasz Sobol
