
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
SOLARIS centre
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
Surface and interface properties of TiO2/CuO thin film bilayers
Thin films, particularly in a form of bilayer, are emerging as potential photocatalysts and photoelectrodes but the challenging aspect consists in the technology and investigation of the interface between both constituents. Thin film bilayers of TiO2/CuO were prepared by means of sequential reactive magnetron sputtering (Figure 1a) in Ultra-High Vacuum (UHV) system. It was demonstrated that under certain conditions both X-ray reflectivity XRR and optical reflectivity measurements can provide information concerning the interfacial properties. X-ray absorption spectroscopy XAS in the surface sensitive mode, i.e., Total Electron Yield TEY, was carried out at SOLARIS centre and allowed to draw conclusions concerning the oxidation state of copper and the electronic structure of the grown materials.
Sequential sputtering performed without breaking a vacuum allows to grow bilayers with a well-defined interface between both components. The thickness of bottom layer (CuO) was about 200 nm (Figure 1b), while top layer thickness (25–150 nm) was controlled by adjusting time of Ti target sputtering. Film roughness of CuO decreased from about 12 nm with the increasing thickness of TiO2 thin film to about 1–2 nm. Surface and interface properties studied with the optical spectrophotometry, X-ray reflectivity XRR and X-ray absorption spectroscopy XAS with soft synchrotron radiation indicated that the bottom CuO layer was completely covered by TiO2 forming p-n type heterojunction but the utmost upper layer was probably Cu-doped TiO2. X-ray absorption spectroscopy demonstrated a presence of Cu+ and Cu2+ in TiO2 top layer of TiO2/CuO heterostructure (Figure 1c). Photoelectrochemical kinetics confirmed that thin film TiO2/CuO bilayers behaved as photocathodes in the photoelectrochemical cell PEC for hydrogen generation (Figure 1d). The values of the photocurrent were found to be dependent on the thickness of TiO2 top layer.
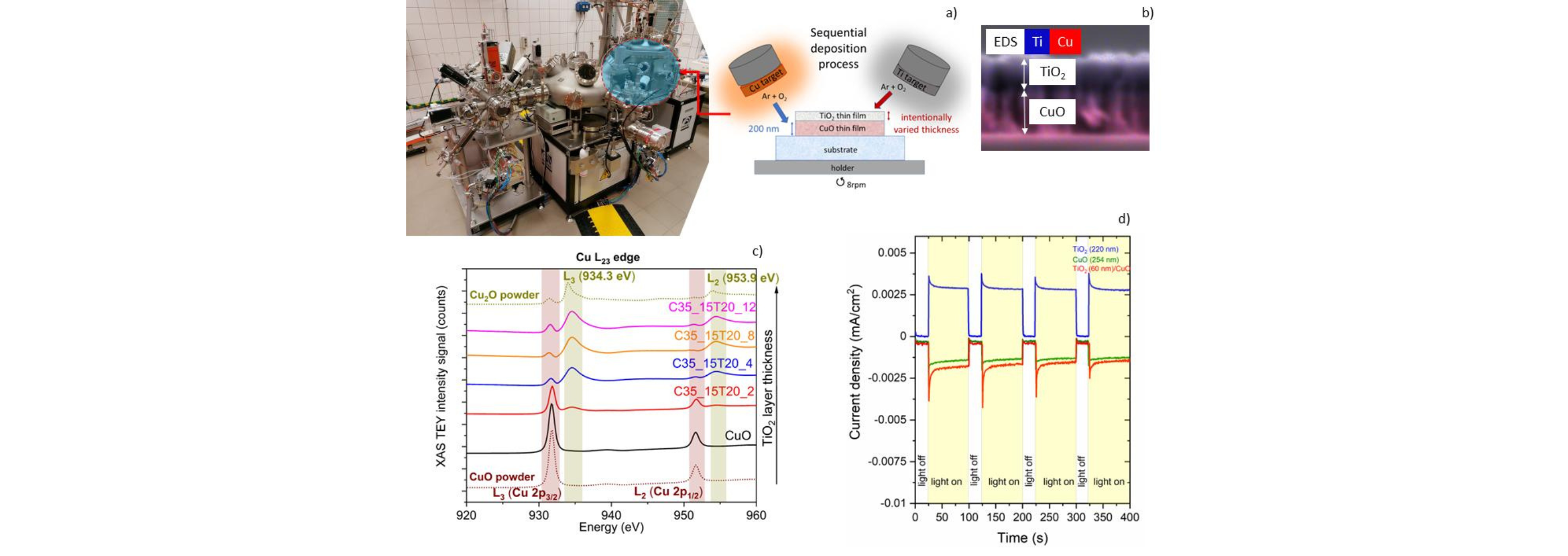
Fig. 1 Ultra- high vacuum UHV system for reactive magnetron sputtering together with scheme of sequential deposition process of TiO2/CuO thin film bilayer a), SEM image of TiO2/CuO bilayer b), X-ray absorption XAS spectra measured at TEY mode at Cu L23 edge for TiO2/CuO heterostructures c), current density vs. time characteristics for: TiO2 thin film photoanode, CuO thin film photocathode and a thin film bilayer TiO2/CuO playing a role of a photocathode d).
The publication can be found here:
