
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
SOLARIS centre
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
 Web Content Display
Web Content Display
Tunable magnetic anisotropy of antiferromagnetic NiO in (Fe)/NiO/MgO/Cr/MgO(001) epitaxial multilayers.
We report on the magnetic properties of antiferromagnetic NiO(001) thin films in epitaxially grown (Fe)/NiO/MgO(dMgO)/Cr/MgO(001) system for different thicknesses of MgO, dMgO. Results of X‑ray Magnetic Linear Dichroism (XMLD) show that together with an increase of dMgO, rotation of NiO spins from in‑plane towards out‑of‑plane direction occurs. Furthermore, we proved the existence of a multidomain state in NiO as a result of competition between the ferromagnet/antiferromagnet exchange coupling and strain exerted on the NiO by the MgO buffer layer.
Recent demonstrations of magnetotransport effects in antiferromagnets (AFMs) make them attractive candidates for usage as active elements in future spintronic devices [1].
We investigated the magnetic properties of antiferromagnetic NiO(001) thin films in epitaxially grown (Fe)/NiO/MgO(dMgO)/Cr/MgO(001) system for different thicknesses of MgO, dMgO. Figure 1 shows exemplary room temperature x-ray absorption spectra acquired with linear polarization of the photon beam, recorded at the Ni2+ L2 edge in the NiO/MgO(18 Å)/Cr. The results of systematic XMLD measurements show that with increasing dMgO, the rotation of NiO spins from in plane towards out of plane direction occurs. The analysis of the XMLD results together with the analysis of low-energy electron diffraction (LEED) pattern, brought us to the conclusion that for NiO layer grown on a wedge-shaped MgO underlayer, the magnetic anisotropy in NiO can be modulated by exerting appropriate strain from its bottom interface.
While strain allows tuning magnetic anisotropy of the AFM from its bottom interface, interaction with the ferromagnetic cover layer enables to influence the magnetic state of the AFM from its top interface. The interfacial exchange coupling between Fe and NiO spins in Fe/NiO/MgO(dMgO)/Cr/MgO(001) was directly confirmed by XMLD- and XMCD- Photoemission Electron Microscope (PEEM) measurements (Fig. 2). The competition between exchange coupling to the ferromagnet and the strain-induced anisotropy creates a multiple domain structure in the NiO thin film.
1.Jungfleisch, M. B., Zhang, W. & Hoffmann, A. Perspectives of antiferromagnetic spintronics. Phys. Lett. A 382, 865–871 (2018).
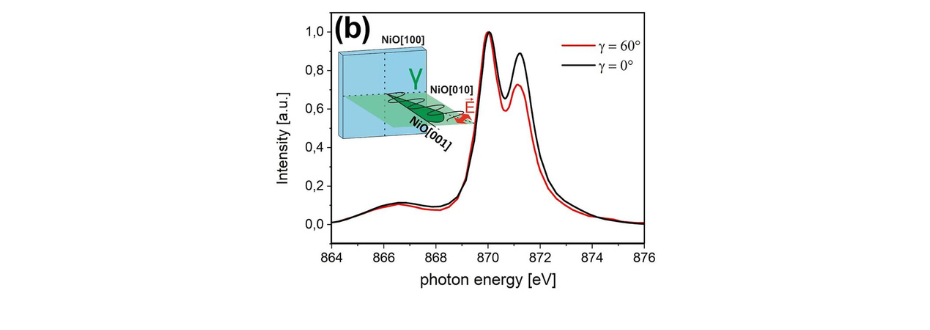
Figure 1. Exemplary Ni2+ L2-edge x-ray absorption spectra at γ = 0° (black line) and γ = 60° (red line) obtained at room temperature for NiO/MgO(18.3 Å)/Cr/MgO(001). The scheme in the inset shows the geometry of the XMLD experiment. (Source: Sci. Rep. 13, 4824 (2023))
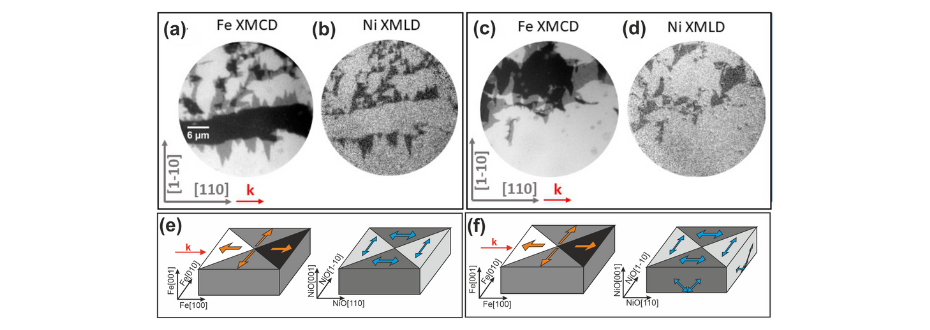
Figure 2. (a, c) The Fe L3 XMCD-PEEM images obtained for Fe/NiO/MgO(10 Å)/Cr and Fe/NiO/ MgO(200 Å)/Cr, respectively. (b) and (d) corresponding Ni L2 XMLD-PEEM images acquired with vertical polarization. (e) and (f) a schematical illustration of spin structure with directions of magnetic moments indicated by the arrows for Fe/NiO/MgO(10 Å)/Cr and Fe/NiO/MgO(200 Å)/Cr, respectively. (Source: Sci. Rep. 13, 4824 (2023)).
Written by: Weronika Janus
The publication can be found here:
W. Janus et al., Tunable Magnetic Anisotropy of Antiferromagnetic NiO in (Fe)/NiO/MgO/Cr/MgO(001) Epitaxial Multilayers, Sci Rep 13, 4824 (2023). doi:10.1038/s41598-023-31930-z
