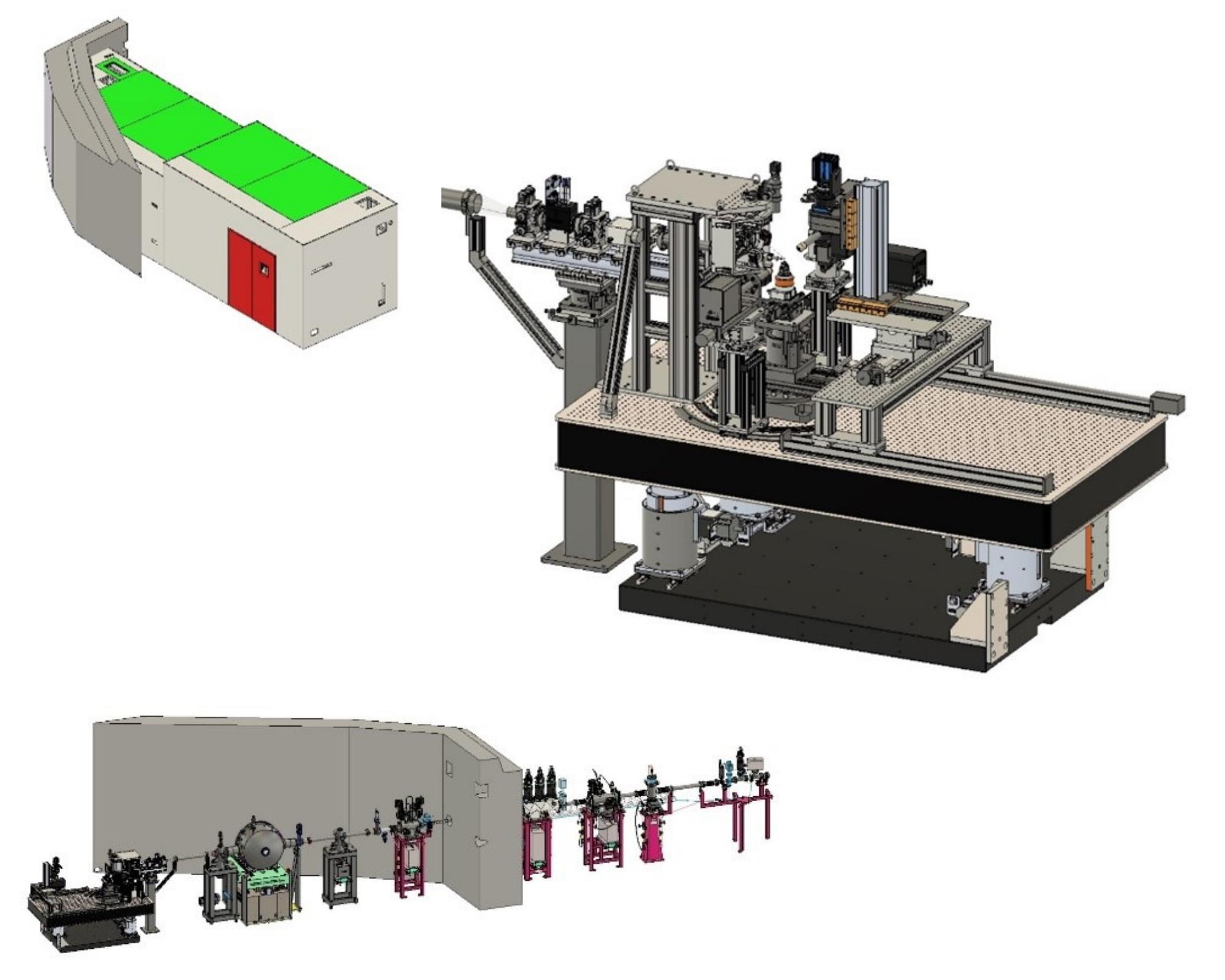
Experimental setup
The experimental setup is placed on a 5-axis optical table (IDT) inside a radiation hutch.
Samples
In standard experiments, samples are placed in air or helium. Non-standard experiments may be performed with user-setups in low or high vacuum or in other gasses. Please, contact POLYX staff for experiment adaptation.
Maximum scanning area (for single large or multiple smaller samples) is 170 mm × 90 mm or 30 mm × 30 mm with an XYZ piezo stage.
Detectors
| Radiography and µCT, XRD |
OptiquePeter X-ray microscope with PCO Edge SCMOS camera with various exchangeable scintillators and objectives 1M Hybrid pixel detector (Eiger 2S 1M) |
| X-ray fluorescence |
Two 80 mm2 Vortex SDD detectors (25 µm Be and ML3.3 Extreme windows) combined with a digital pulse processor DANTE (XGLAB) that enables mapping and recording of whole XRF spectra without deadtime in continuous snake-like scans |
| X-ray absorption spectroscopy and X-ray emission spectroscopy | Two von Hámos geometry-based spectrometers equipped with cylindrically bent silicon crystals and charge-coupled devices (CCDs) suited for time-resolved spectroscopy |
| Beam monitors & transmission |
Ionization chambers, PIN diodes |
| Sample inspection | On-line and off-line optical microscopes for sample inspection and scan range definitions |
Data acquisition and position capture is performed with PandaBox (Quantum Detectors).
Limitations
While planning experiments at POLYX, users must bear in mind the limitations of the beamline.
Polycapillary and monocapillary optics generate high flux at the expense of short working distances of 2.5 mm – 40 mm. This may make some types of experiment difficult.
Due to relatively soft spectrum of SOLARIS bending magnet and presence of beamline window, the energy spectrum of the beamline is limited to 4-15 keV. Hence, X-ray radiography and tomography is limited to rather soft or small samples. For X-ray absorption and X-ray emission spectroscopy only elements with K-, L- and M-edge binding energies falling between 4 keV and 15 keV are accessible. For XRF, the X-ray emission lines with energy of >1 keV must be selected, and elements with emission lines >15 keV can be excited only using white beam excitation.